
So to submit changes, first fork the main repo, then push the changes to your fork, and then create a pull request to get the changes from your fork merged into the main repo. Due to security reasons, you can't submit changes directly to the main version of the repo.
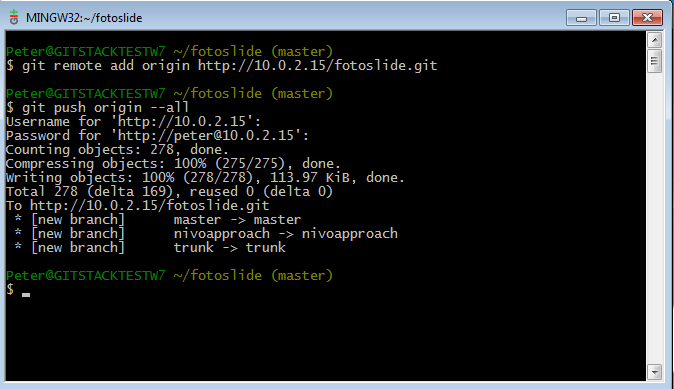
Git remote add how to#
This is required for you to submit change requests to the main version of the repo (we'll learn how to create a pull request later on).

You should first make a fork of each repo you want to work on. It is possible to do the two things separately, but in practice you will nearly always do them together when contributing to other people's projects.

GitHub is a web application that provides useful tools on top of Git for working with stored codebases, as well as server space to store the codebases.It allows a group of developers to work on the same code base without getting in each other's way, stores the code base safely in a remote location, allows developers to roll the code back to previous states if required, and more. Git is a version control system tool - an essential class of tools in any development workflow.The following are essential concepts that you must be familiar with to get the most out of Git and GitHub.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
